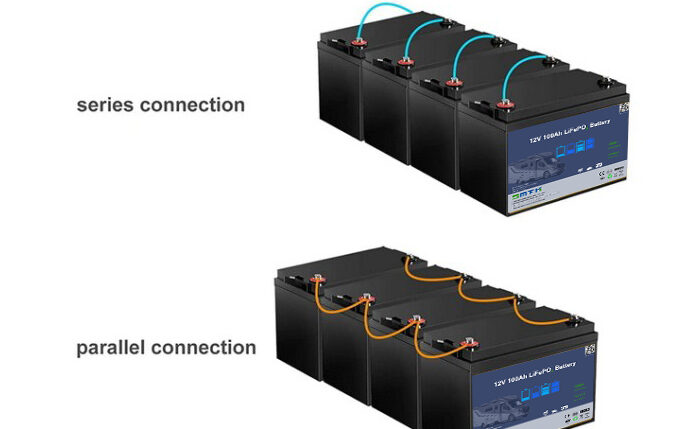
There are two main configurations for battery connections: series and parallel.
What is a Series Connection?
– Definition: Connecting batteries in series means connecting the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of another, increasing the total voltage output while maintaining the same capacity.
– Advantages: Ideal for applications that require a higher voltage than a single cell can provide.
When to use a series connection?
– High voltage applications: When devices require a higher voltage than a single battery cell can provide, e.g. eight 3.2V LiFePO4 batteries connected in series provide a combined voltage of 25.6V.
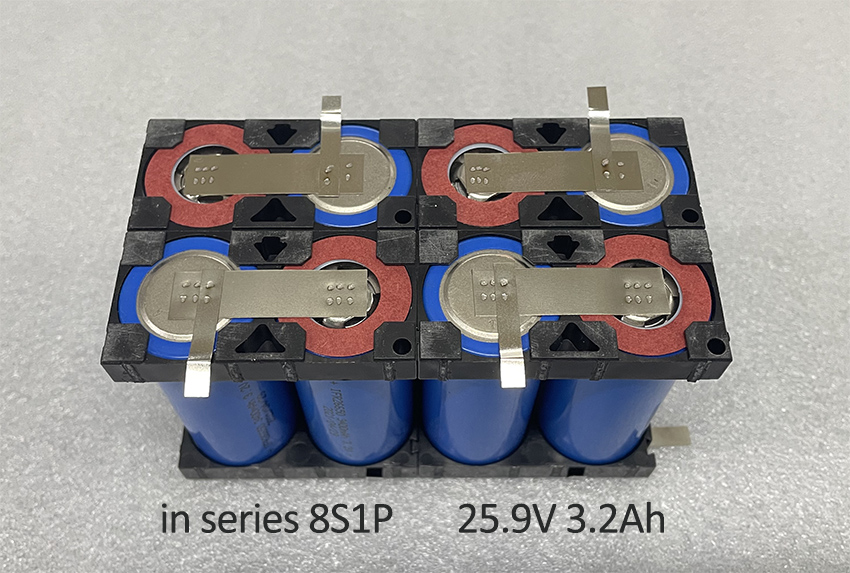
– Consistent battery quality: Ensuring that all batteries in the series have the same capacity and are at the same state of charge to prevent imbalances.
What is Parallel Connection?
– Definition: A parallel connection involves connecting the same terminals of multiple batteries together to increase the total capacity.
– Advantages: Suitable for applications that require increased capacity and run time without increasing voltage.
When to use a parallel connection?
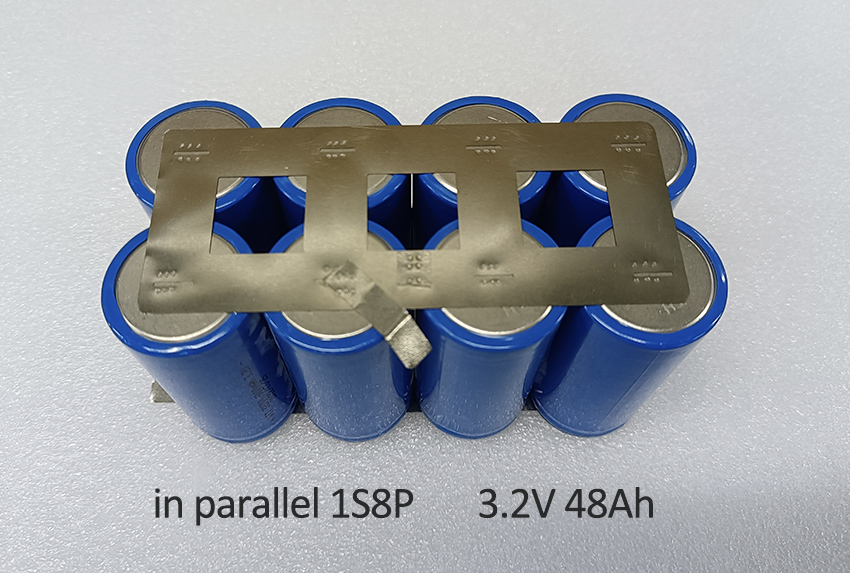
– High capacity requirements: When charging LifePO4 batteries in parallel, the voltage remains constant while the capacity (or ampere-hours, Ah) of the battery increases as the voltage increases.For example, if you have eight 6Ah LiFePO4 batteries in parallel, the combined capacity is 48Ah, but the LifePO4 charge voltage remains the same as a single battery.

Series and Parallel Considerations
– Compatibility: Use batteries with the same voltage and capacity ratings to avoid problems.
– Protection: Implement a battery management system (BMS) to monitor and balance the health and performance of the battery pack.
By understanding the distinct advantages of series and parallel connections, you can tailor your lithium battery setup to effectively meet specific energy needs. SmarTEC offers customized service. You can customize the energy (Wh) and power (W) densities of your battery pack to meet specific needs, such as electric vehicles or stationary energy storage systems.

